Industry Theory Core: Meso-Management Principle for Enterprises
As the competition among Chinese enterprises enters a new phase, new theories are needed to guide business operations and enhance competitive advantages within the industry.
The theory of industry essence forms the foundational theory for the meso-management of enterprises within the new productive forces framework.
In the field of economic research, the concept of "meso" was explicitly introduced by Dr. Hans-Rudolf Peters from the former Federal Republic of Germany's Eadenberg University, who specialized in meso-economics and structural policy as well as economic system theory. He posited that the main starting point of structure theory and structure policy lies in economic sectors, regions, and industries, which serve as intermediate aggregates between the micro and macro scales. He argued for the establishment of an independent theory in this realm to address the factors affecting the development of economic structure at the sectorial and regional levels. This classification not only delineates a clear scope for meso-economics but also sets defined boundaries for micro and macro economies.
Meso-economics acts as a bridge linking macro-economics and micro-economics. Together, micro-economics, macro-economics, and meso-economics constitute a holistic economic framework. Meso-economics arises from practical needs, as it studies economic behavior and operational mechanisms at the sector and regional levels. Former Dean of the School of Economics and Management at Shanxi Normal University, Professor Zhou Yangming, asserted in his writings that meso-economics is guided by macro perspectives while being grounded in micro foundations.
Although the Chinese theoretical community has called for research into meso-economic issues and explored meso-economic phenomena, a meso-economics suitable to China's national conditions has yet to be established. The study of meso-economics focuses on the economic behavior and operational mechanisms of sectors and regions. To date, meso-economics has not developed into a relatively independent system and remains a weak link in economic theory.
Similar problems exist within enterprise management theory, where ambiguous boundaries or disconnects are evident between macro-strategic management and micro-tactical management. For instance, if a team's goal is to go out and catch rabbits (macro management), in an era when rabbits are plentiful (product supply exceeds demand), possessing rabbit-catching skills (micro management) allows the team to succeed simply by stepping outside. However, in a scenario where there are too many teams hunting rabbits (overly competitive market) and the rabbit population is dwindling (product supply exceeds demand), merely having the skills to catch rabbits (micro management) may not guarantee success. In such cases, it is critical first to identify where the rabbit burrows are and the primary activity zones of the rabbits. Only by determining these aspects can a team improve its chances of catching rabbits. This identification of rabbit burrows and activity zones falls neither under macro-strategic management nor micro-tactical management, which I refer to as meso-management.
In enterprise management, a common saying goes: "Focus on both ends while managing the middle." However, in practical management, emphasizing macro-strategic goals can lead to neglect of micro-tactical execution, and vice versa. This explains why economists often struggle with effective business management and entrepreneurs rarely transition successfully into economic theorists.
Thus, meso-management has become key to effective enterprise management.
In enterprise operations, meso-management (meso management) involves the management of the business direction, aligning the goals of national economic and social development with the strategies of specific industries and enterprises to outline the trajectory and work plans for business growth.
Meso-management is not only a component of macro management, facilitating connectivity but also determining the direction of micro-management under the guidance of macro strategies. The quality of meso-management plays a crucial role in the success or failure of macro management. However, without the guidance of macro management, the effectiveness of meso management may be compromised. Macro management serves as the strategic framework for enterprises, and both meso and micro management rely on this foundation, complementing one another symbiotically. Absent effective meso-management, optimal management goals cannot be achieved, no matter how well micro and macro strategies are implemented.
Meso-management is born from practical necessity. It sets the direction for micro-management and determines the success or failure of macro management. The essence of the industry in enterprise management serves to define the strategic direction for businesses, ultimately determining the effectiveness of their strategies. The theory of industry essence posits that the essence of industry dictates the scale of profit or loss, influencing the survival of enterprises. Therefore, in a sense, the theory of industry essence forms the foundational theory of meso-management in enterprises.
Research on meso-management within enterprises, akin to meso-economic studies, requires familiarity with macro management while possessing rich micro-level knowledge and multi-industry management experience. Although systematic studies on meso management in Chinese enterprises have yet to take shape, some researchers have begun relevant work. The enterprise positioning management that gained popularity over a decade ago is, in essence, a form of meso-management aimed at defining the development direction of certain operational elements. For instance, Professor Lu Changyuan's proposal of slicing marketing fits within the realm of enterprise positioning management and forms part of meso-management and industry essence theory in determining business development direction.
Currently, research in Chinese meso-economics has not yet formed a relatively independent theoretical framework and remains a weak link in economic theory. Comparatively, research on enterprise meso-management lags even further behind meso-economic studies. A review of extensive literature revealed a dearth of academic research and media coverage on enterprise meso-management, with hopes that the study of industry essence theory will pave the way for advances in meso-management within Chinese enterprises. Just as venturing out to sea for fishing (macro strategic management) necessitates navigating with a fishing vessel, nets, and hooks into deeper waters (micro tactical management), accompanied by skilled fishermen onboard (micro-management), we also need to take along a compass and a migration route map for fish (meso management) to enhance the success rate and profitability of fishing in a crowded ocean with dwindling fish stocks (achieving macro strategic goals).
Meso research serves to examine the implementation of strategies and tactics, fitting between macro and micro studies while emphasizing the integration of theory and practice. Characteristics of meso research include:
First, mediatory nature. Meso research is less about the recognition and rational thinking typical of macro studies or the detailed analysis characteristic of micro studies, striving instead to identify solutions for specific issues.
Second, duality. Meso research builds on macro studies, drawing from micro study materials, bridging the two, ensuring that both maintain their practical relevance and yield normal and accurate results at specific scales.
Meso research breaks free from the constraints of experiential and localized narrowness in practice, finding depth and scale in problem-solving, allowing for a more comprehensive representation of quantitative and qualitative developments.
Features of meso research include a focus on comparative analyses of macro environments impacting specific trends while also emphasizing theoretical consistency and practical impact; its proximity to social practice contrasts it with purely academic inquiry; and it provides guidance in navigating the interplay between theory and practice, offering correct problem-solving directions at specific scales.
The theory of industry essence serves as the foundational theory for enterprise meso-management, determining the direction of micro-management and influencing the success or failure of macro strategy.

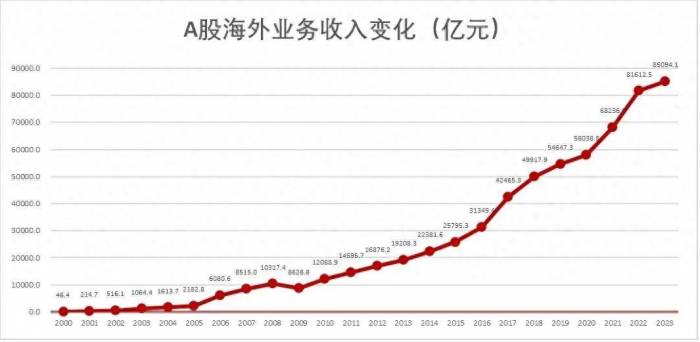

























Join the Conversation